Discover the future of IoT
Overcome the limitations of wireless connectivity
While IoT has changed the way we interact with the world around us — Its application is challenged by a number of key factors that are stunting its potential.
In the near future, more than 30 billion of devices will be connected with the internet. As the number of devices and data traffic increase, the spectrum becomes more crowded. Interference problems become worse, causing the network to potentially lose a large amount of data and thus relevant information.
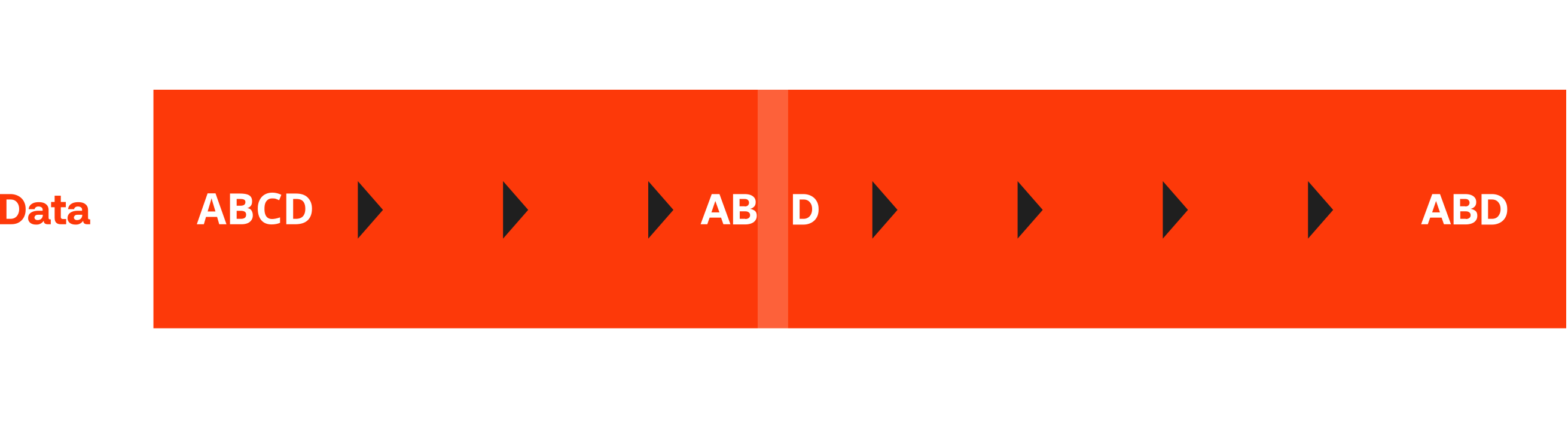
Proprietary wide area IoT connectivity solutions, such as traditional LPWAN technologies are especially impacted by this trend. These technologies were developed for point-to-point connectivity, but not for large-scale deployments. This approach makes them vulnerable to interference. They are also characterized by a variety of issues that can impede transformational change.
Limitations of today’s available LPWAN
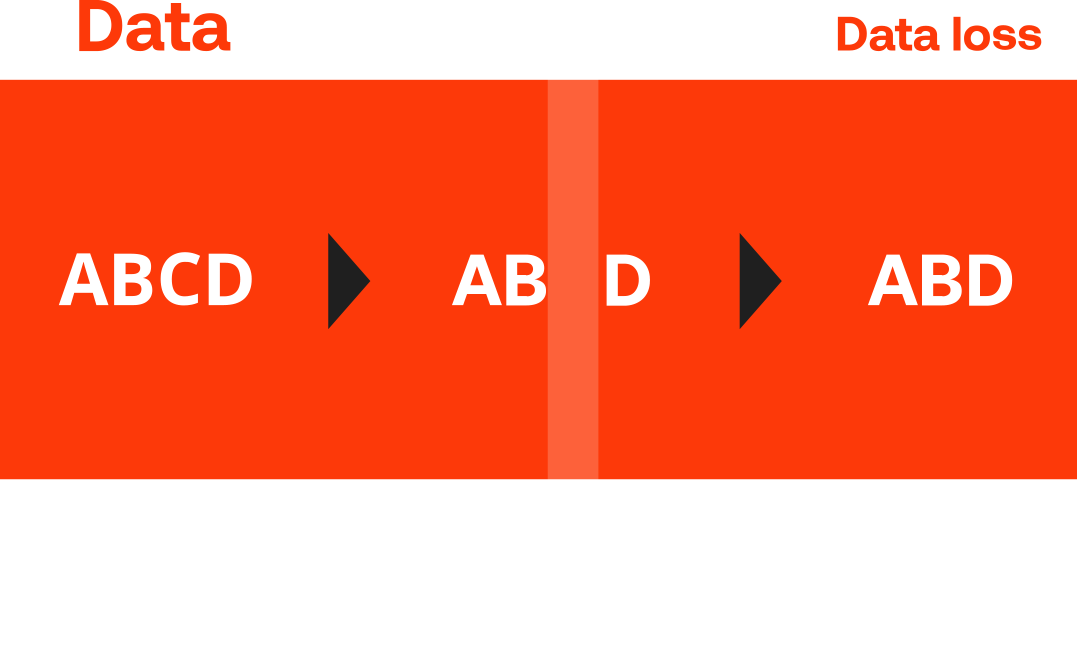
Especially proprietary medium range and wide area IoT connectivity solutions, such as meshed networks and traditional LPWAN technologies, transmitting data wirelessly in license free bands are affected of this trend. These technologies were developed for point-to-point connectivity, but not for large-scale deployments. That approach makes them not only vulnerable to interference. They are characterized by a variety of issues impeding transformational change.
Limitations of today’s available LPWAN
The mioty technology
mioty is a software based low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) protocol that was developed to overcome today’s and future wireless connectivity limitations. With its best-in-class reliability and scalability, mioty is designed for massive industrial and commercial IoT deployments.
The core invention behind the mioty technology is the Telegram Splitting Multiple Access (TSMA) method. As defined by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI TS 103 357), Telegram Splitting splits the data packets to be transported in the data stream into small sub-packets at the sensor level.
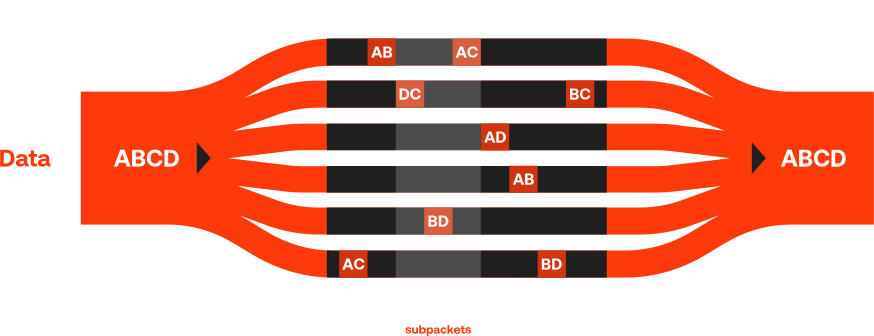
These sub-packets are then transmitted over different frequencies and time. An algorithm in the base station permanently scans the spectrum for mioty sub-packets and reassembles them into a complete message. Due to sophisticated Forward Error Correction (FEC), the receiver only needs 50% of the radio bursts in order to completely reconstruct the information. This reduces the impact of corrupted or lost bursts due to collisions and increases the resistance to interference.
The mioty technology
mioty is a software based low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) protocol that was developed to overcome today’s and future wireless connectivity limitations. With its best-in-class reliability and scalability mioty is designed for massive industrial and commercial IoT deployments.
The core invention behind the mioty technology is the Telegram Splitting Multiple Access (TSMA) method. As defined by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI TS 103 357), Telegram Splitting splits the data packets to be transported in the data stream into small sub-packets at the sensor level.
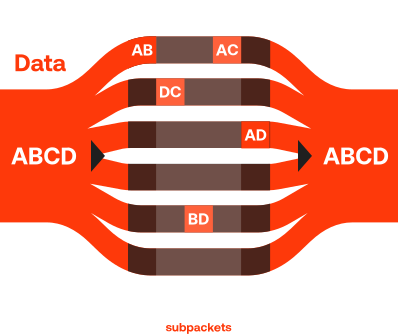
These sub-packets are then transmitted over different frequencies and time. An algorithm in the base station permanently scans the spectrum for MIOTY sub-packets and reassembles them into a complete message. Due to sophisticated Forward Error Correction (FEC), the receiver only needs 50% of the radio bursts in order to completely reconstruct the information. This reduces the impact of corrupted or lost bursts due to collisions and increases the resistance to interference.


